One of the things we see frequently mentioned on the Forex news websites is the term "safe haven currencies." This usually represents the currencies to which inventors and traders turn in times of uncertainty or economic downturn, states Konstantin Rabin of investfox.com.
When discussing safe haven currencies, the first currency which comes into mind for the majority of the market participants is the US dollar. In fact, the American currency is not only a safe haven currency but also the world’s top reserve currency as well.
It goes without saying that this has some significant implications for the Forex market as well. One of the prevalent trends during the last couple of decades is the fact that in times of global recession, the US dollar tends to recover and even make some notable gains.
In order to illustrate one example of this, we can take a look at this daily GBP/USD chart, which shows the price movements of this pair before and after the 2008 Financial Crisis:
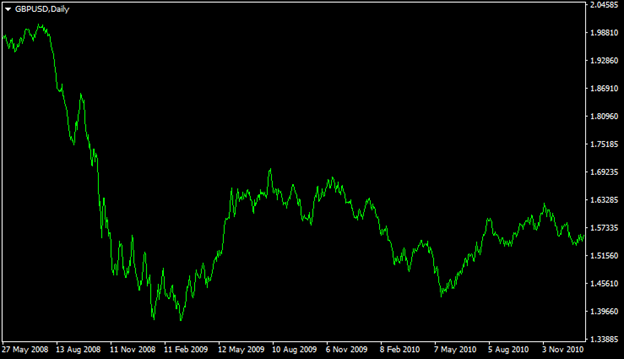
As we can observe from the above diagram, back in May 2008 the GBP/USD pair was trading close to the $1.97 level. During the following months, the British currency made some gains and eventually reached the psychologically important $2.00 level.
However, as time went on it became more and more apparent that the world economy was not dealing with a local recession or temporary economic setback. Instead, it soon became very obvious that the world’s economy was in a deep recession and at that time it was not at all clear whether or not this would have turned out to be the beginning of the depression as well.
As we can see from this chart, this great deal of uncertainty has led to a sharp appreciation of the US dollar. As a result of this development by the end of this year, the GBP/USD currency pair has dropped all the way down to the $1.40 level. As it became more or less clear to the market participants that global depression was averted, the pound recovered. However, the pound never reached the 2008 highs again.
Other Examples of USD Strength in Times of Economic Uncertainty
Here it is important to point out that the exchange rate movements of the GBP/USD pair during the 2008 Financial Crisis is not the only example that shows the role of the US dollar as a safe haven. There are many other examples as well. We can take a look at one of them, by observing yet another GBP/USD chart, which covers the period before and after the outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic:
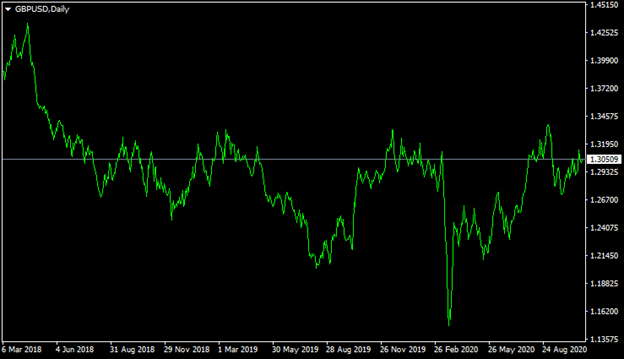
As we can see from the above diagram, during the early Spring of 2018, the GBP/USD pair was trading close to the $1.38 level. Initially, the British currency has made some notable gains, eventually rising all the way up to $1.44 by April 2020. However, those gains eventually turned out to be temporary. From the following month, the GBP/USD currency pair began its long-term decline, eventually dropping down to the $1.19 level in the course of Summer 2019. However, at that time the British pound managed to regain its strength and eventually return to the $1.30 level.
Now, this is exactly the point when the outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic has started to have a significant impact on Forex and the stock market. As a result, in a very short space of time, the GBP/USD pair has dropped all the way down to the $1.15 mark, a level not seen in several decades.
One of the main reasons for this decisive move was the fact that in March 2020, it was very uncertain what effect the outbreak of the pandemic would have on the state of the world economy. It was quite obvious that at least a short-term recession was unavoidable. However, the main question faced by the majority of the market participants was whether or not this would be the beginning of yet another great recession just like back in 2008.
During the subsequent months as the world economy began to recover, the GBP/USD pound began to rise and once more returned back to the $1.30 level. So as we can see here the US dollar tends to appreciate in times of economic uncertainty, yet it might decline once things return back to normal. In fact, there is yet another example, which shows the effects of the USD being a safe haven in the Forex market. This is apparent on this daily EUR/USD chart:
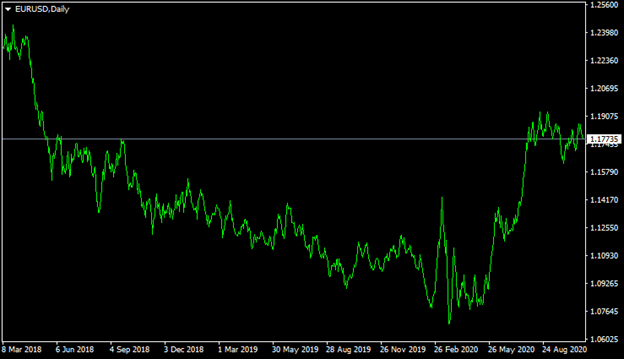
As we can observe from the above diagram, back in March 2018, the EUR/USD pair was trading close to the $1.25 level. However, in the late Spring 2018, the Euro began its long-term decline. After quite a long period of a downward trend, the single currency tried to rally and regain its recent losses during early 2020. However, due to the uncertainties brought about by the outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic, this attempt has failed. Instead, the EUR/USD exchange rate fell sharply, dropping all the way down to the $1.06 level.
Just like in the case of the GBP/USD pair, as things stabilized and the worst-case scenario was averted, the EUR/USD pair has recovered and now trades close to the $1.18 level.
Reasons Behind the Safe Haven Status of the US Dollar
At this point, many might have an obvious question: What are the reasons behind the safe haven status of the US dollar? Well, firstly it is important not to forget that the US dollar is backed by the strongest economy in the world. Obviously, this is not a 100% guarantee of the strength of the US dollar, but this makes it highly unlikely for the currency to collapse and for millions of people to lose their savings as a result. The fact of the matter is that the US government has never defaulted on its debt obligations. In addition to that, the US dollar has been the world’s reserve currency for more than 70 years.
All those factors contribute to the confidence investors and traders have in the US dollar as a stable currency. It is also worth noting that the US dollar is the most liquid currency in the world. So if an individual wants to sell the US dollar in order to buy some local currency and purchase some things, the process is very simple. The US dollar is widely accepted in banks and money exchange bureaus.
On the other hand, if the market participant has some exotic currency, then it might be very difficult to exchange it for a major currency since in some cases financial institutions in that particular country might be unwilling to accept the given currency. In sharp contrast to those currencies, the US dollar is widely accepted by all financial institutions.
It is also helpful to mention that the average long-term inflation rate going back all the way back to 1913 is nearly 3%. Obviously, achieving this for a couple of years might not be that difficult, but having such a track record for more than a century is indeed very impressive. Therefore, many savers and investors use the US dollar as a store of value as well, before they make any investment into stocks, bonds, real estate, or other assets.
Now, under normal circumstances, the market participants who are aware of the effects of inflation do want to invest their capital into profitable investments in order to preserve their purchasing power and hopefully even grow it to a certain extent.
However, in times of economic downturn and uncertainty, this goal takes a backseat and it becomes more important for the market participants to simply hold on to their net worth. As a result, what many investors do is sell off their investments in other currencies and convert them into the US dollar, until they can get a better idea about the possible economic future.
Influence of Safe Haven Status on Exchange Rates of the US Dollar
So the next logical question which we have to explore is: how does the safe haven status of the US dollar affect its exchange rates in the Forex market? Well, firstly it is important to make it clear that what we have concluded above does not mean that the US dollar only appreciates in times of economic uncertainty and crisis. The reality of the matter is that the standard rules apply to the US currency as well.
This means that generally speaking higher real interest rates tend to benefit the US dollar. Here in this case it is not only the US real interest rates that matter, but also the fact how they compared with the real interest rates in other major economies.
For example, here it is useful to remember that two periods of significant USD strength were from 1995 to 2001 as well as from 2014 until 2020. In both cases, the real interest rates in the United States were considerably higher than in the Eurozone, Japan, Britain, and other economies.
For example, by 2000, the US federal funds rate had reached 6.5%, when the European Central Bank’s key interest rate started at 3% at the time the Euro was first officially introduced. There was no financial crisis of global proportions during the late 1990s, however, the US dollar has still managed to rally and reach multi-year highs against the US dollar, the Euro, the British pound, and many other currencies in the Forex market.
We had a similar situation during the second half of the 2010s. The fact of the matter was that by the end of 2018 the US Federal Reserve had raised its key interest rate all the way up to 2.5%.
Now, this might not seem like a high-interest rate. However, it is worth noting that during this period the European Central Bank held its key interest rate at 0%. The Bank of England has only increased rates to 0.75%, while the Bank of Japan kept rates at -0.1%. Consequently, it is not surprising that this state of affairs has given a sizable advantage to the US dollar in terms of real interest rate differentials.
We talk about the real interest rate differentials, rather than nominal interest rates. This is because there are several emerging market currencies, which did have much higher nominal interest rates than 2.5%, but this did not turn out to be the case. For example, by October 2020, the Turkish central bank has its key interest rate at the 10.25% level.
So if the nominal interest rates were the decisive factor in determining the exchange rates, then it would have been logical to expect a massive appreciation of the Turkish lira against the US dollar. However, it did not happen. Instead, during the last three years, the Turkish currency has depreciated by more than 90%.
One of the main reasons for this is that the average inflation rate in Turkey is well above 10%. Therefore, despite this large nominal interest rate differential, the real interest rates in the US are still higher than in Turkey, hence the appreciation of the USD/TRY exchange rate. This example shows that when it comes to the Forex exchange rates it is the real interest rate that matters more than the nominal rates.
So when there is no financial crisis in the world, it is the relative real interest rates and other important indicators which determine the long-term exchange rate movements in the Forex market.
In addition to that, such economic indicators as the real gross domestic product growth rate, the unemployment rate, and the consumer price index all have a certain degree of influence on the Forex market. This is why it is always helpful for market participants to analyze all of the important fundamental and technical indicators before making any trading decisions.
By Konstantin Rabin of investfox.











